


Communication means sending and receiving a message that produces a response. In other words, it is a two-way process of exchanging ideas or information. The process of communication becomes effective when it achieves the desired response.
6 Essential components of communication are:
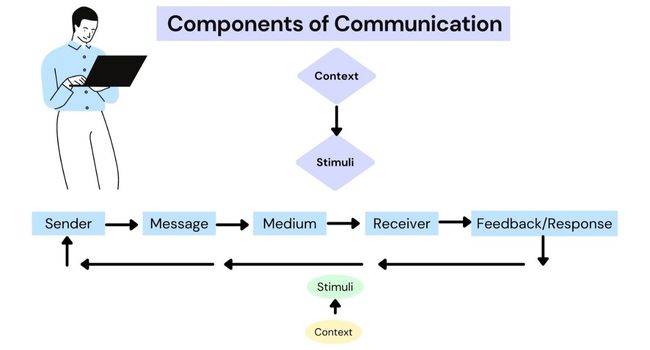
Every message begins with context. Context means including country, culture, organization, and external and internal stimuli. Every country, every culture and. every company or organization has its own way of processing and communicating information. Another view of context is the external stimulus such as a letter, memo, fax, or telephone.
Its response may be oral or written. It influences how you translate your ideas into a message. You express behaviors, opinions, and emotions through communication. You represent past experiences, likes, and dislikes. Education, job status, and confidence are also ways of communication.
In the communication process, a sender is a person who sends a written or oral message. There are external as well as internal factors that prompt the sender to design a message. He selects symbols/words to convey his message. So, the receiver may understand it. He reacts as he desires. A sender chooses suitable symbols to convey his message. Likewise, it is his decision that is the most effective medium for his message.
It is the main idea that you want to communicate; it is of both verbal symbols and nonverbal symbols. The important thing is to decide exactly what you want to say. The receiver of your message is also important.
Medium means the way by which you communicate a message. You can choose electronic mail, printed words, or sound. The relationship between the sender and the receiver affects the choice of medium. The spoken medium depends upon the urgency of a message. Here are the important features of oral and written communication.
| Sr. | Oral Communication | Written communication |
| 1 | Prompt reply/feedback | Delayed reply/feedback |
| 2 | Informal style | Formal style |
| 3 | Extempore and informal language | Conventional language |
| 4 | Emphasis on interpersonal relationship | Emphasis on the content of the message |
| 5 | Cannot be used for permanent record | It is useful for permanent record |
Internal communication includes written memos and reports. It involves bulletins and job descriptions. Posters, notes, employee manuals, and electronic bulletin boards are examples. Even internal faxes are internal communication. Oral communication consists of staff meeting reports, face-to-face discussions, presentations, audiotapes, telephone chats, teleconferences, or videotapes.
External written communication includes letters and reports. Telegrams, cablegrams, and mailgrams are examples. External communication involves faxes, telexes, postcards, and contracts. Ads, brochures, catalogues, news releases, etc are also its components. It is a face-to-face discussion. Telephone or presentations in the oral scenario is its part.
The receiver/decoder of your message is your reader or listener. A message may have more than one receiver. They receive messages through their eyes and ears. Thus, non-verbal factors such as touch, taste, and smell influence them.
Feedback (oral/written) is a reply to a message. It is also an action like receiving in the mail an item you ordered. We also use silence as feedback, though it is not very useful. Senders need feedback to determine the success or failure of the communication.
Here are three stages of the process of communication.

In this diagram, according to O. Donnell, the communication process becomes complete. But most of the experts feel stressed that there must be a response. That’s why it is incomplete or ineffective communication.

In this style of communication, the sender also receives the response or feedback. This is complete communication.

Sometimes noise creates a disturbance in the communication process. Thus, the receiver does not receive a clear message. This is defective or disturbed communication.
An exchange of messages results in a reaction means communication. In other terms, it is a two-way process of exchanging thoughts, information, and context. Context is the first element of any message. The context covers country, culture, structure, and external and internal stimuli.
There is the communication process. The sender is an individual who transmits the written or oral message. The fundamental notion conveys both verbal and nonverbal symbols, according to the message. Medium: The method used to convey a message and refers it to as medium. You have the option of using sound, written word, or e-mails.
Written memos, reports, and bulletins are internal communication. Internal communication also covers job descriptions, posters, and notes. Other examples of internal communication are staff manuals and electronic bulletin boards. We can not ignore one other part is the internal fax.
One thought on “Components of Effective Communication to Complete the Process of Communication”